Guide de démarrage avec pygeoapi¶
pygeoapi est un outil pour publier rapidement et facilement les services OPEN API OGC sur le web. Il est construit sur les puissantes bibliothèques open-source de la communauté (géo)python.
Dans ce guide de démarrage, nous vous guiderons dans la mise en place du logiciel et l’utiliserons pour certains cas spécifiques. Le long de la route, nous allons nous engager avec certains logiciels connexes, parce que pygeoapi est un produit qui est généralement combiné avec d’autres composants pour répondre à un besoin commercial.
Connaissances préalables¶
pygeoapi est une application Web Python pour le domaine spatial, vous devez donc être conscient des concepts d’applications Web et les aspects géospatiaux tels que les formats raster et vectoriels, les normes OGC et les systèmes de projection. La connaissance de Python est recommandée, bien que vous puissiez vous en passer en exécutant l’application à partir d’OSGeoLive.
Contenu
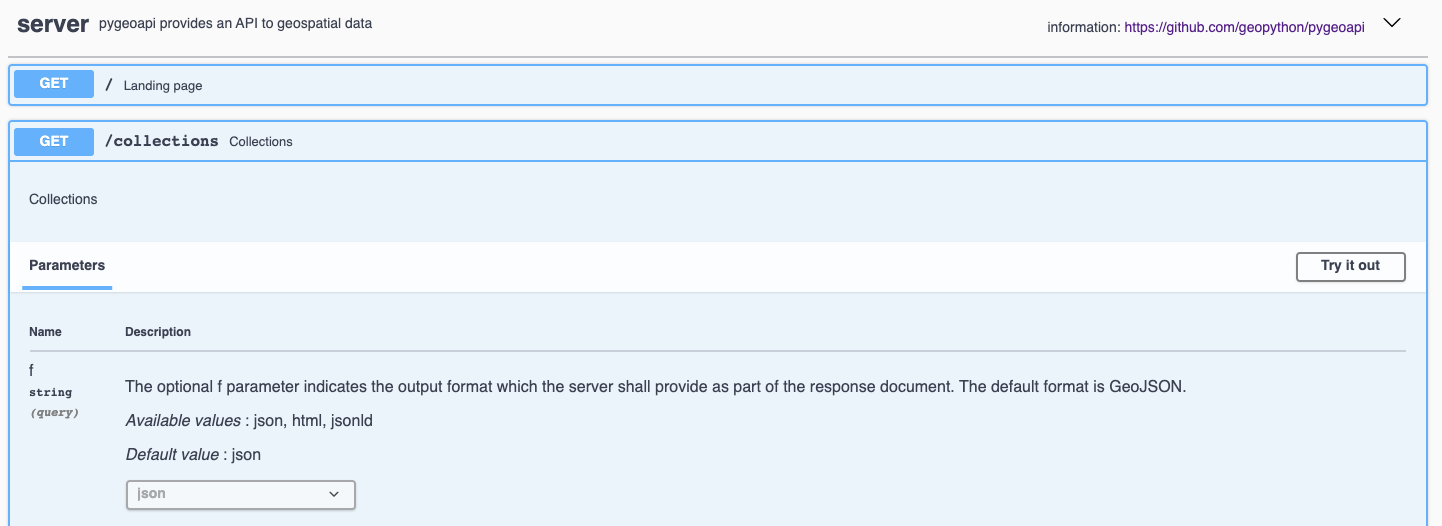
Configurer et démarrer le service¶
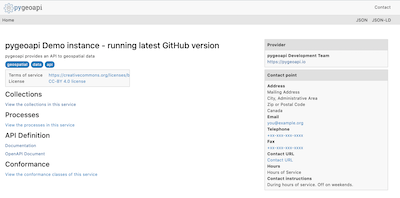
À partir du menu Démarrer, sélectionnez . L’application ouvrira une page Web à l’adresse http://localhost:5000
naviguer dans le dossier utilisateur
/usr/local/share/pygeoapiet localiser un fichierpygeoapi-config.yml. Ce fichier contient la configuration du service.Ouvrez le fichier avec la commande
sudo nano pygeoapi-config.yml.Mettez à jour certains paramètres du fichier, tels que le titre et l’auteur. Et enregistrez le fichier.
Redémarrez le service, par exemple en fermant le terminal et en redémarrer le service
Configurer un nouveau service¶
Vous allez maintenant déployer un ensemble de données vectorielles dans pygeoapi et exposer ses fonctionnalités en tant qu’API OGC - Features. OGC API - Features est une norme d’OGC pour exposer les entités vectorielles en tant que service Web. OGC API - Features est l’alternative OpenAPI à WFS.
pygeoapi prend en charge un large éventail de backends à utiliser comme source vectorielle, par exemple géopackage, PostGIS, Elasticsearch, WFS, etc. Via le fournisseur GDAL OGR, un ensemble presque illimité d’autres sources vectorielles peut être ajouté.
Interesting datasets to expose as OGC API - Features consist of real world data having multiple attributes and links to other resources.
OSGeoLive contains a number of datasets we can use. An example is /var/www/html/openlayers/examples/data/geojson/countries.geojson.
You can configure it in pygeoapi using the GeoJSON provider.
Téléchargez le fichier GeoJSON et placez-le dans le dossier tests/données.
Update
pygeoapi-config.ymlto addcountriesas a new collection to pygeoapi (insert snippet below between the other collections. Mind the nesting, nesting is important in YAML syntax).
countries:
type: collection
title: Countries
description: Countries of the world
keywords:
- industry
links:
- type: text/html
rel: canonical
title: information
href: https://openlayers.org
hreflang: en-US
extents:
spatial:
bbox: [-180,-90,180,90]
providers:
- type: feature
name: GeoJSON
data: /var/www/html/openlayers/examples/data/geojson/countries.geojson
id_field: name
Redémarrer pygeoapi
Vérifiez que la collection est disponible via votre navigateur à l’adresse http://localhost:5000/collections/countries
Utilisation d’un navigateur Web pour interroger l’API¶
Now that we have the service available we can query it using various client tooling.
Each of the features of the collection is available in common formats, such as HTML, GeoJSON and GML. To start we can use a web browser to browse through the service. From http://localhost:5000/collections/countries, drill down to individual features. The service will automatically detect (accept header) that you are using a web browser and will return the HTML representation of features. Notice in the top right corner explicit links to override the accept header and request specific representations of the feature (?f=json).
Chaque Open API dispose d’une page de documentation interactive http://localhost:5000/openapi. Dans cette page Web interactive, vous pouvez lire sur les différentes méthodes du service, mais aussi interagir directement avec eux via des formulaires Web.
OGC API’s have been developed with the W3C Spatial Data on the Web Best Practices in mind. An important aspect of these best practices is search engine optimization. Pygeoapi adds some crawl optimizations on top of the requirements of the Open API standards; collection metadata can be crawled by search engines in a structured way, with the goal to make the collections discoverable in tools like Google Dataset Search. To evaluate the structured data capabilities you can use the Structured Data Testing tools of Yandex or Google. Copy the html source of the countries collection page (or the url of a collection page of an online pygeoapi instance) into a structured data testing tool and evaluate what structured data the tool is able to extract from it. The search engine will use that information in its datasets index.
Using OGC API - Features in Desktop GIS¶
Dans ce guide de démarrage, nous utilisons QGIS pour interroger le service, mais un flux de travail similaire est possible dans d’autres outils SIG, par exemple ArcGIS, FME, OpenLayers.
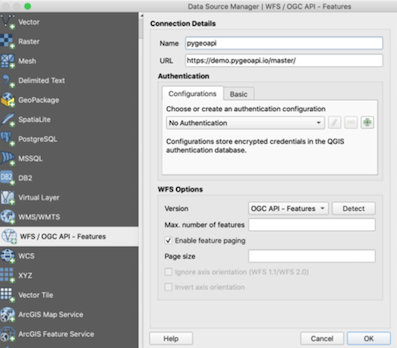
Starting from QGIS 3.14 you can add an OGC API - Features layer as vector layer. From the Layer / Add Layer menu select Add WFS Layer....
Sur la fenêtre qui s’ouvre, créez une nouvelle connexion, entrez l’url au service http://localhost:5000.
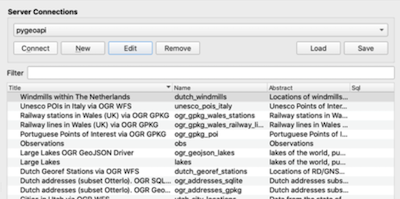
Cliquez sur Ok, puis connect pour charger les collections disponibles dans le service.
Sélectionnez la collection countries et cliquez sur ‘Add’ pour ajouter la couche dans la carte QGIS.