
Kosmo - Desktop is a user friendly, desktop GIS application which allows you to explore, edit and analyse spatial data from a variety of databases, vector and raster formats.
This Quick Start describes how to:
Contents
In order to start the application, follow the next steps:
From the start menu, select Geospatial ‣ Desktop GIS ‣ Kosmo
The application will take a few seconds to start (a splash screen is shown while loading)

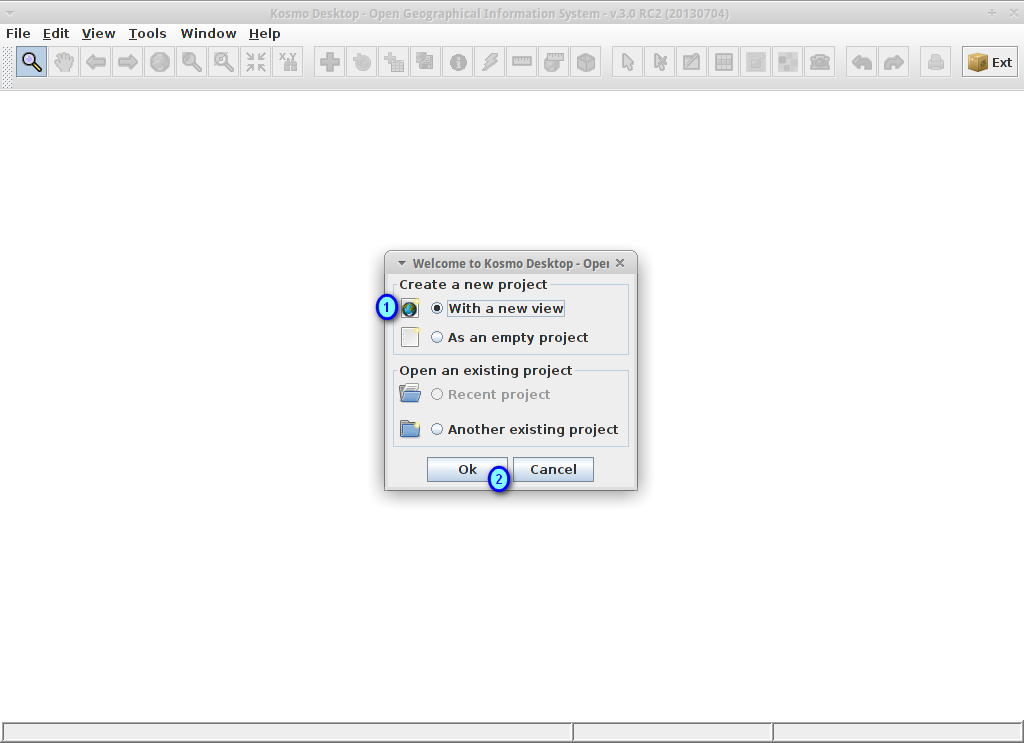
In the Welcome dialog, select the option Create a new project ‣ With a new view (1) and press the Ok button (2)
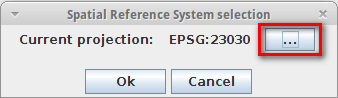
In the Spatial Reference System selection dialog, press the ... button
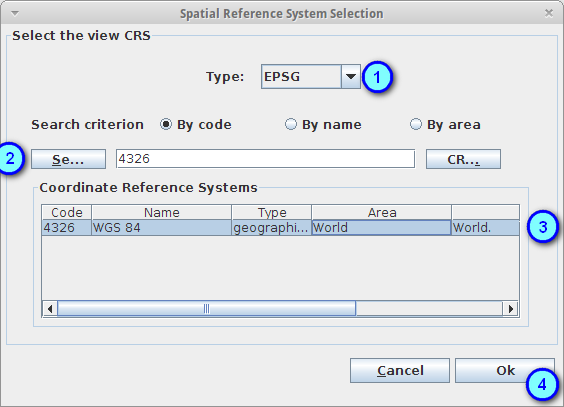
Select the option EPSG in the SRS type combobox (1), insert the text 4326 in the text field and press the Search button (2)
Select the SRS EPSG:4326 - WSG4 (3) and press the Ok button (4)
Press the Ok button again to select the SRS loaded. The view will start with EPSG:4326 as the base projection
Tip
You can see which projection has been selected as base for a specific view in the view window title bar, right to the view name
The Kosmo Desktop main window has the following sections:
Main menus
Main toolbar
Layer tree
Tree that contains the categories and layers that have been loaded in the current view.
Map
Status bar
Shows the application warning messages to the user.
Current cursor coordinates
To start out, we’re going to load some of the sample data included on the OSGeo-Live DVD:
Choose the option View > Load Dataset... or push the button with the green plus from the main toolbar
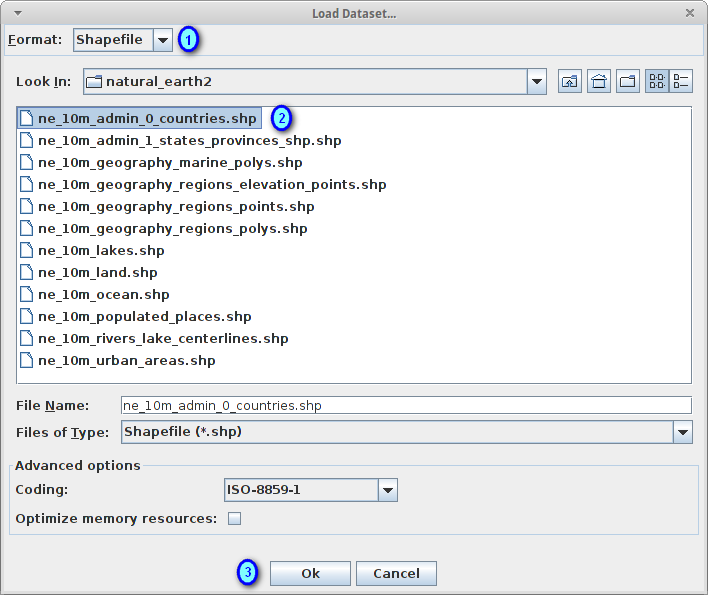
In the Format combobox, select Shapefile (1)
In the file chooser, select the file ne_10m_admin_0_countries.shp from the directory /home/user/data/natural_earth2 (2)
Press the Ok button to load the selected shapefile (3)
In the layer tree, press the visibility checkbox to make the layer visible, right clicking on the Working folder if needed
Choose again the option View > Load Dataset... or push the button with the green plus from the main toolbar
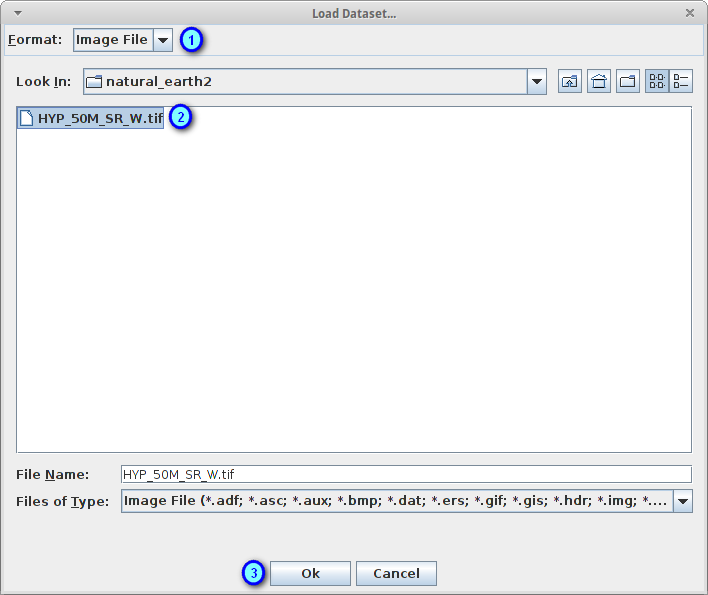
In the Format combobox, select Image file (1)
In the file chooser, select the file HYP_50M_SR_W.tif from the directory /home/user/data/natural_earth2/ (2)
Press the Ok button to load the selected image file (3)
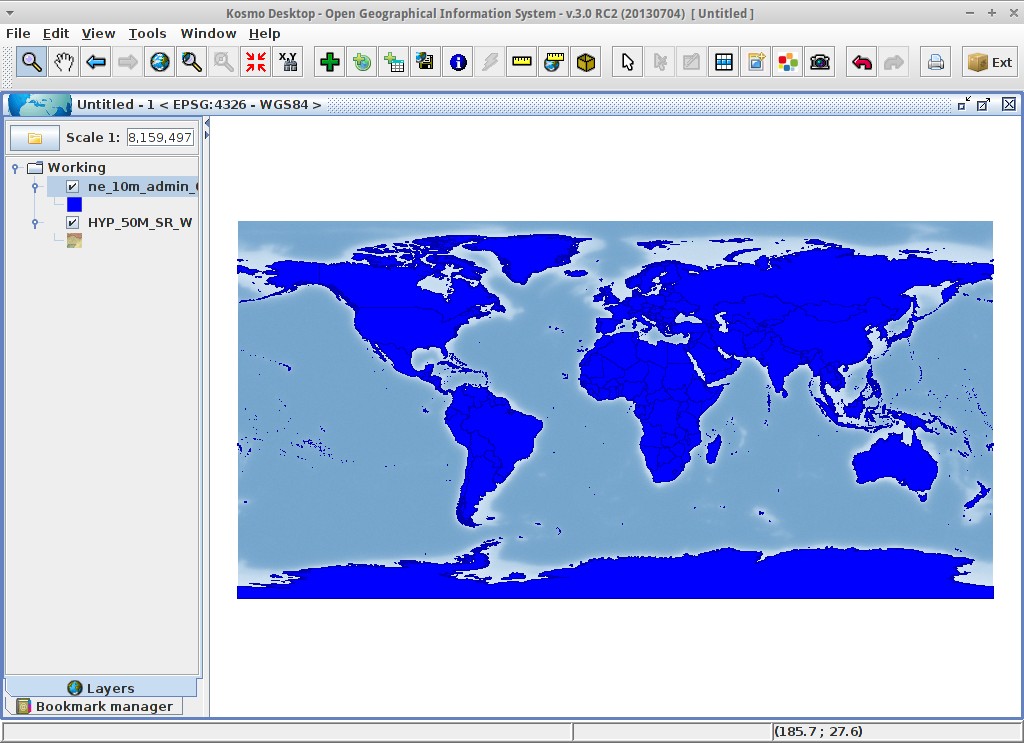
In the layer tree, press the visibility checkbox to make the layer visible
You can see that the layer drawing order is from bottom to top in the layer tree: modify the layer order by dragging them in order to show them properly
Note
The OSGeo-Live DVD contains some file data examples in the following directories:
You can try to load more examples from those directories. Remember to select the correct format from the Format combobox
Tip
It’s possible to add all the images from a directory as an unique layer by selecting the parent directory in the Load Dataset... dialog: Kosmo Desktop will load them as a mosaic.
We’re going to load a database table as an example:
Choose the option View > Load Dataset... or push the button with the green plus from the main toolbar
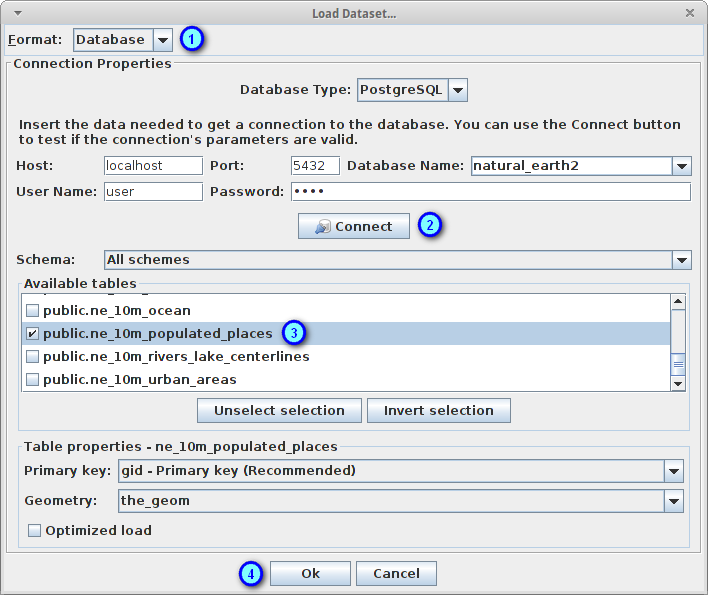
In the Format combobox, select Database (1)
Fill the fields host, port, database name, user name and password with the values:
Press the Connect button to load the tables present at the natural_earth2 database (2)
Select the checkbox corresponding to the table ne_10m_populated_places (3)
Press the Ok button to load the selected database table (4)
In the layer tree, press the visibility checkbox to make the layer visible

Start the GeoServer WMS included in the OSGeo-Live DVD by selecting the option Geospatial ‣ Web Services ‣ GeoServer ‣ Start GeoServer (or from the desktop, go into Web Services folder and double-click the Start GeoServer icon)
Press the Load SDI Service (IDE) button at the main toolbar to open the wizard
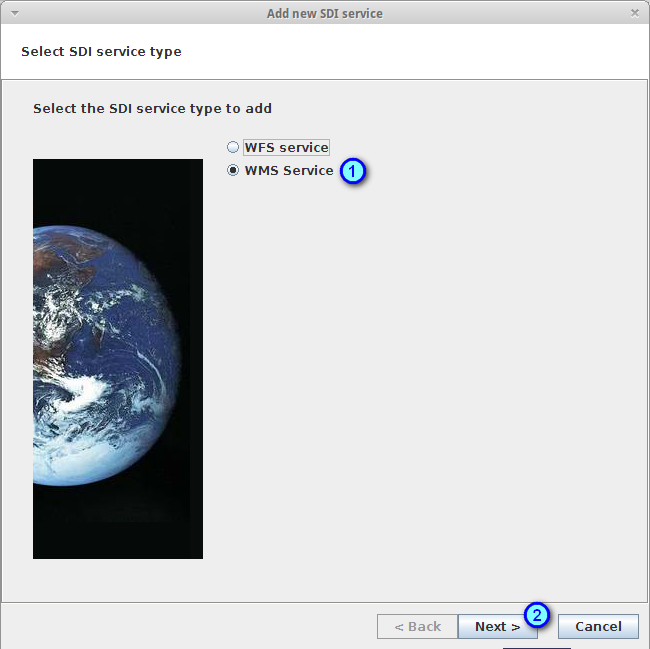
In the Select SDI service type panel, select the option WMS Service (1) and press the Next button (2)
In the Select Uniform Resource Locator (URL), type the URL http://localhost:8082/geoserver/ows? in the corresponding text field (1) and press the Connect button (2)
If the connection is successful, press the Next button to go to the next panel (3)

Select the layer North America Sample Imagery (1) and press the > button (2) to move it to the right list. Press Next button. (3)
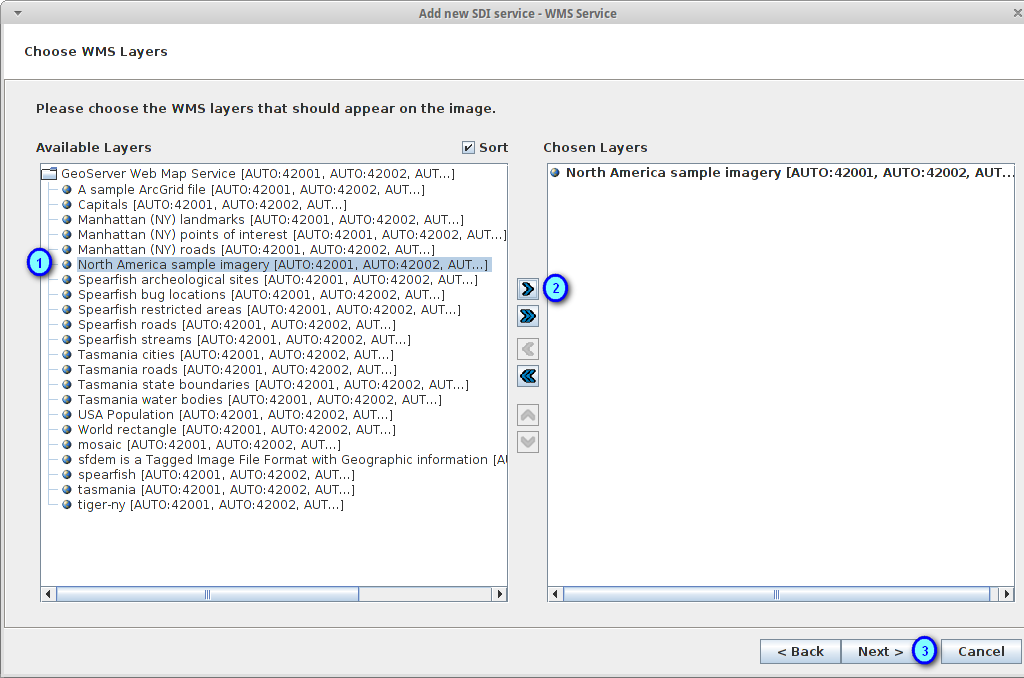
Leave the default options loaded and press the Finish button (1) to start the layer loading
In the layer tree, press the visibility checkbox to make the layer visible
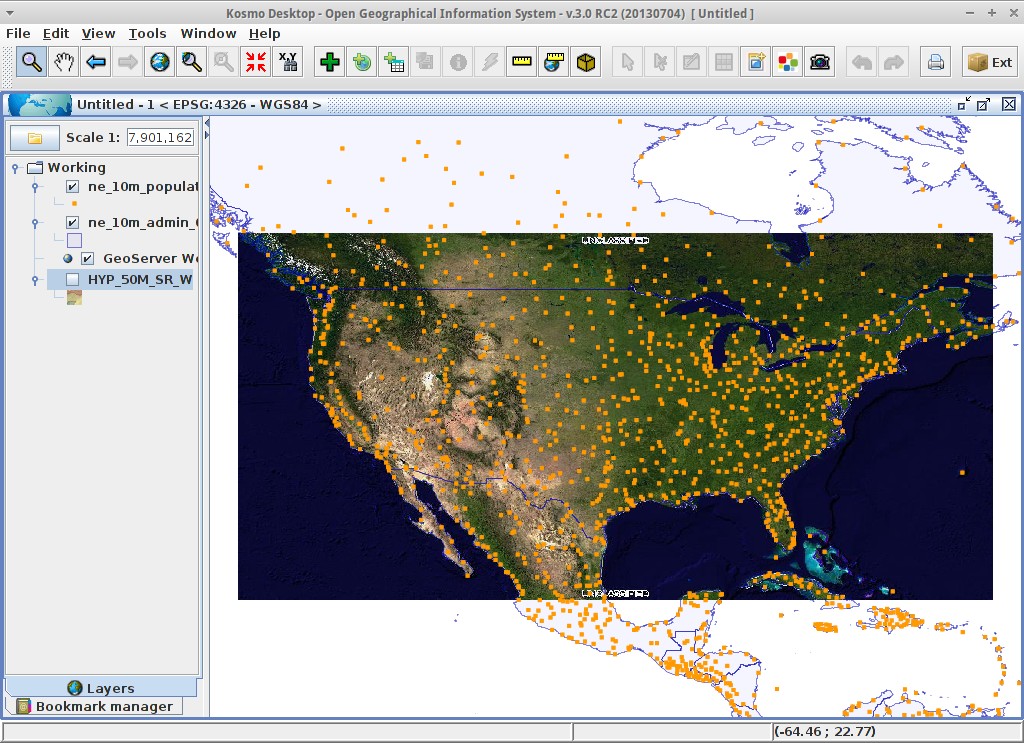
Select the layer in the layer tree and press the Zoom To Layer button to center the map in the WMS layer view
Reorder the layer tree by dragging the new layer and put it over the HYP_50M_SR_W raster layer
Note
Kosmo Desktop contains a set of lists of WMS servers by default, divided into locations (most of them are from Spain). If you’re connected to internet, you can use them as described in the example with the local server.
In this section we’re going to style a layer by range using the country population as styling attribute:
Select the layer ne_10m_admin_0_countries in the layer tree
Right click on it and select the option Simbology > Change Styles...
Click on the tab Colour theming
Activate the options Enable colour theming (1) and by range (2)
Select pop_est as Attribute (3), 11 as Range count (4) and RYG (Color Brewer) as Color schema (5)
Press the Ok button to apply the changes (6)

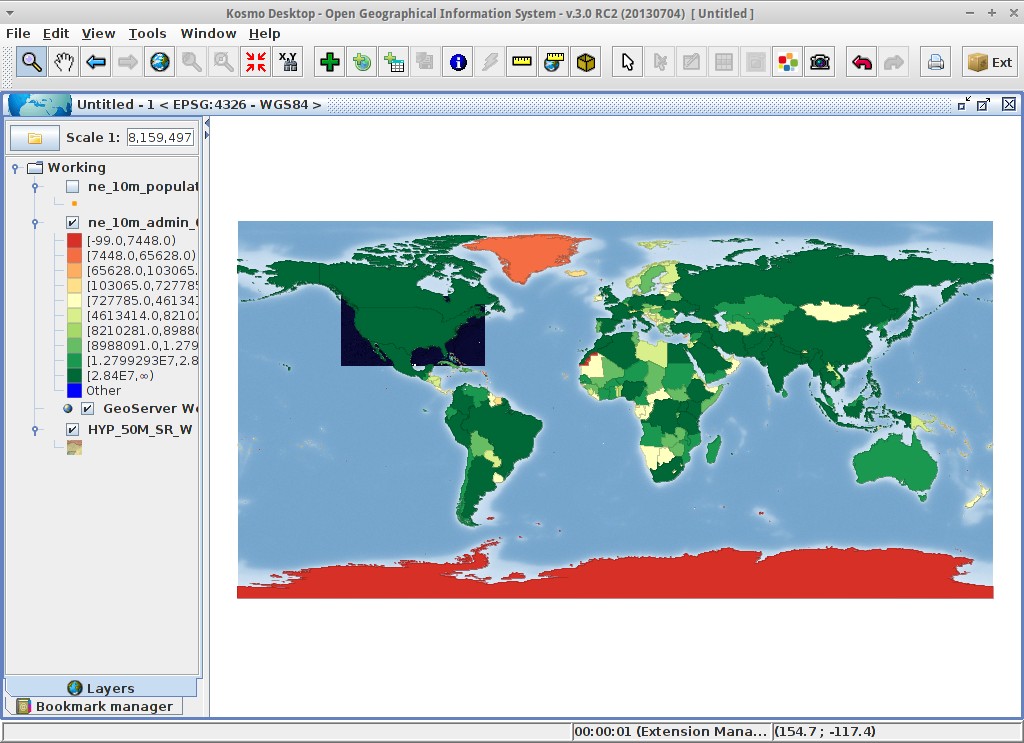
The layer will change its style to reflect the changes:
In this section we’re going to style a layer with some rules and filters, based on an attribute. The example shows how to create two rules, one for capital populated places and other for the rest of them:
Select the layer ne_10m_populated_places in the layer tree
Right click on it and select the option Simbology > Advanced Style Editor...
Select the feature type style ne_10m_populated_places (1) and press the + button (2) to add a new rule to it
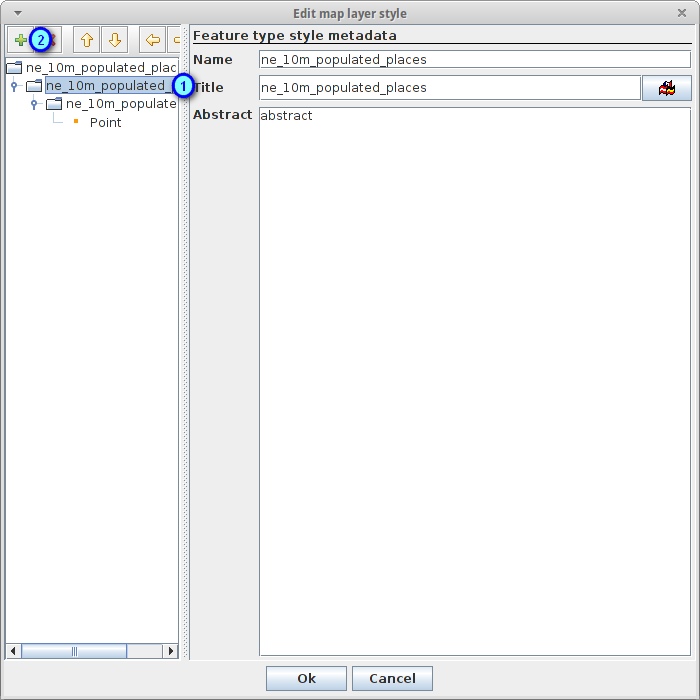
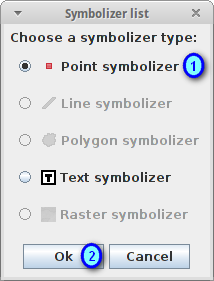
Select Point symbolizer as symbolizer type (1) and press the Ok button (2)
Select the new rule in the tree (1) and edit its properties: set capital_rule as Name (2), Capitals as Title (3),activate its filter (4) and edit it (5)

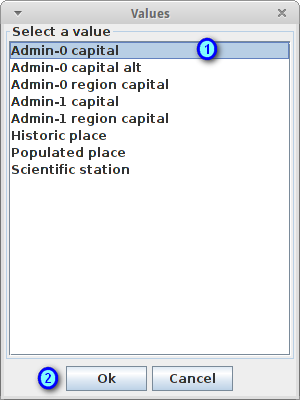
Select featurecla as Field (1), Equal to (=) as Operator (2) and press the ... button (3) to select an attribute value

Select the Admin-0 capital value (1) and press the Ok button (2)
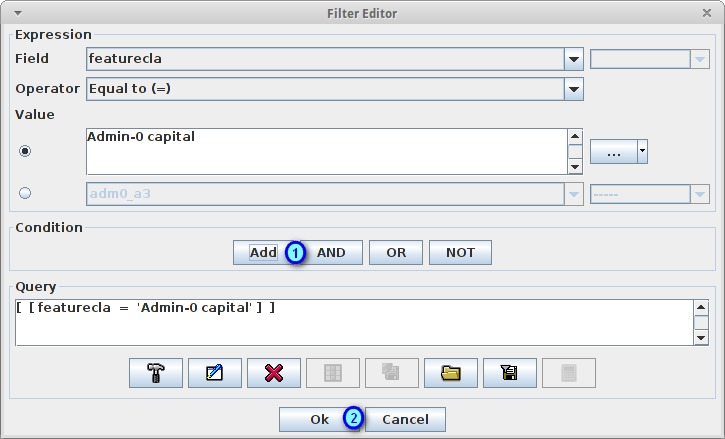
Press the Add button (1) to add the condition to the filter and the Ok button (2) to set the filter to the rule
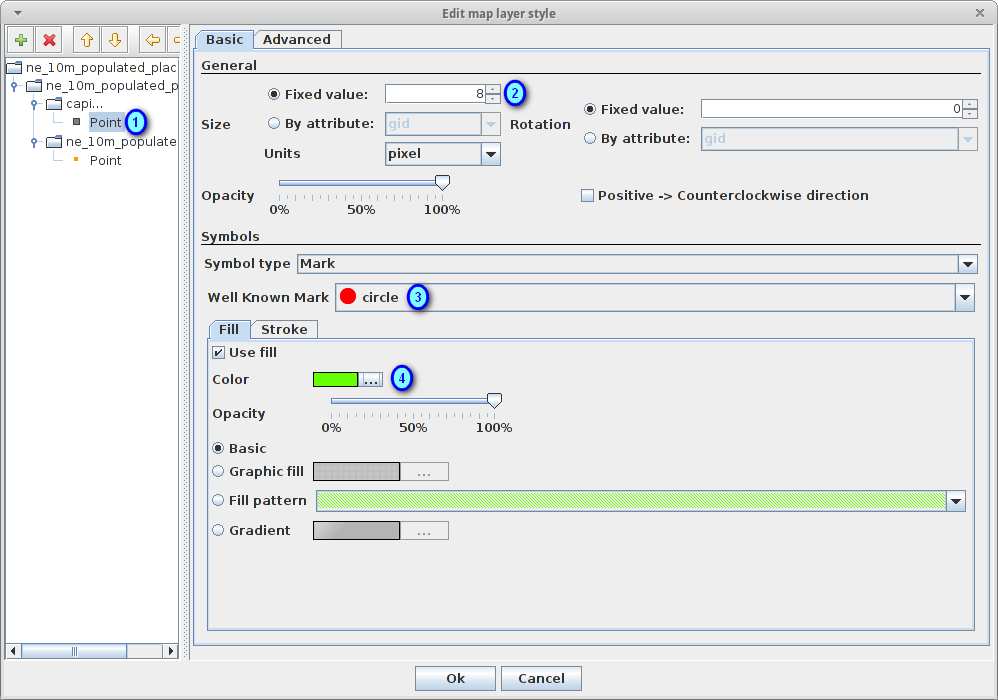
Select the capital rule point symbolizer in the tree (1) and edit its properties: set its Size to 8 (2), its Well Known Mark type as circle (3) and Color to light green (4)
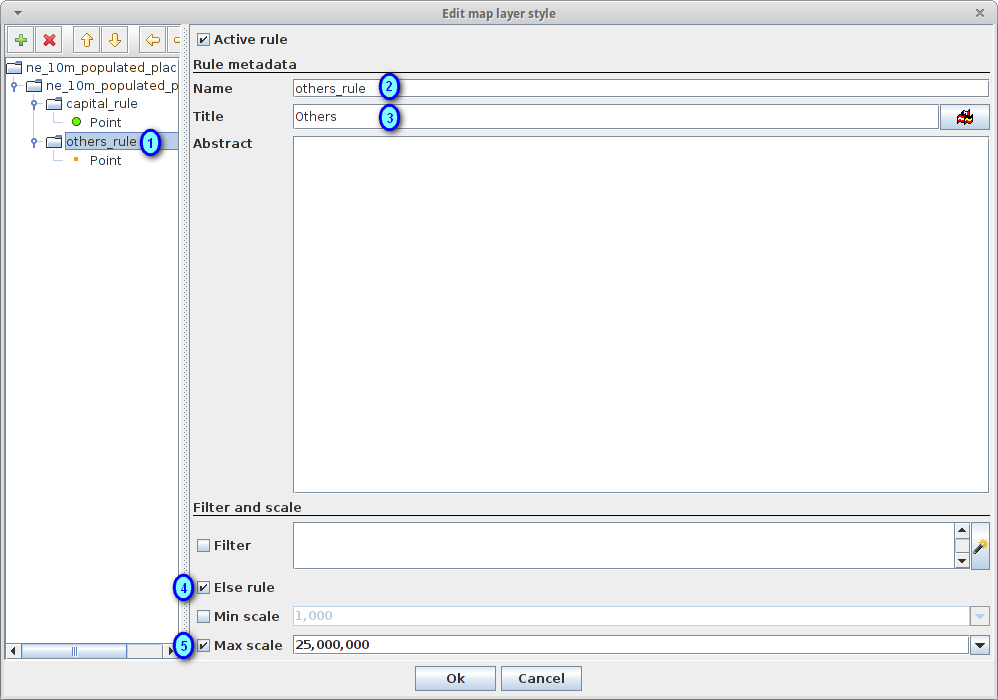
Select the other rule in the tree (1) and edit its properties: set others_rule as Name (2), Others as Title (3), mark the Else filter checkbox (4) and set its maximum scale to 25,000,000 (5) (it’s necessary to press ENTER key after setting the value manually to set it)
Press the Ok button to apply the changes
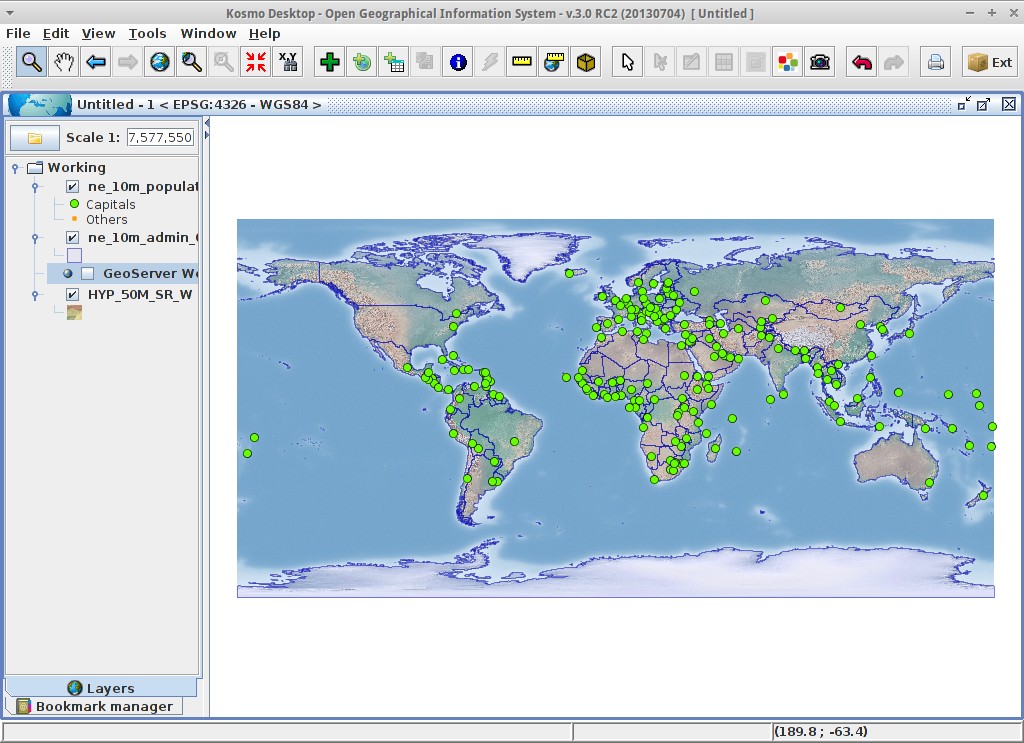
The layer will change its style to reflect the changes:
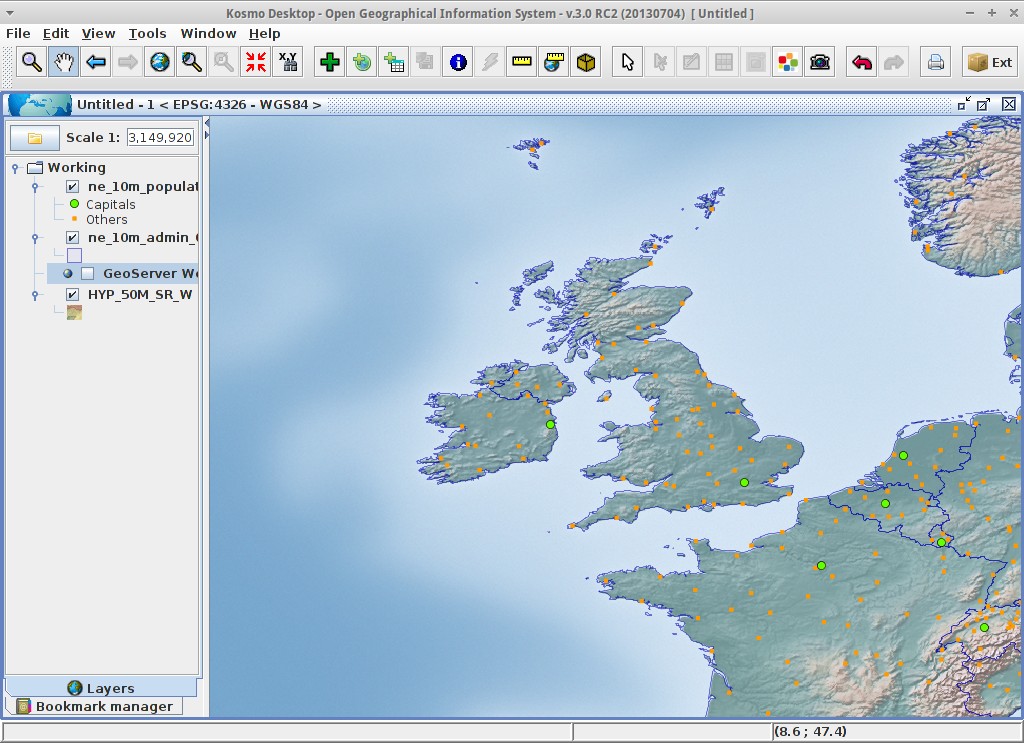
If you make enough zoom in to reach the given scale, both rules would be rendered:
Note
When the map is at full layer scale only capitals are shown. If you zoom in close enough, all the populated places would be shown
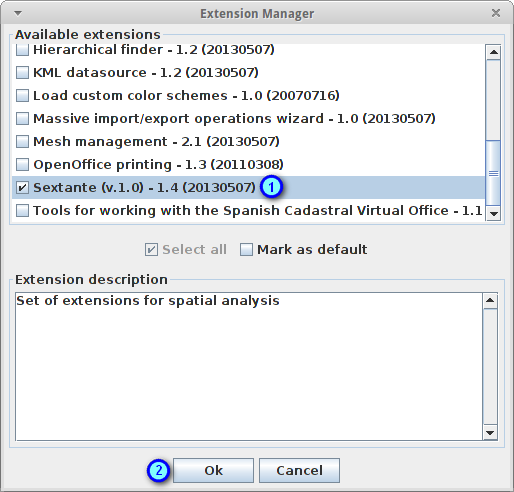
In this section we’re going to activate the Sextante toolbox extension:
Choose the option File > Extension Manager... or push the button with the Ext label from the main toolbar
Mark the Sextante extension checkbox (1) and press the Ok button (2)
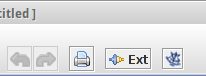
A new Sextante button will be available at the right of the main toolbar
Tip
If the Mark as default option is selected, the extension would be loaded automatically on next application startup
Here are some additional challenges for you to try:
There is a set of manuals and video-tutorials available at http://www.opengis.es/index.php?lang=en